Back
Oct 30, 2023
•
General Wallet Use
•
7 min
Leather users now have access to Stacks multisig support via Asigna – a native multisig solution for Bitcoin and Stacks.
This latest update effectively makes Asigna the first native multisig wallet for the Stacks Bitcoin layer with a BTC-native approach that emphasizes added security for users. Leather and ALEX are the first apps to incorporate Stacks multisig.
Read on for more on multisig transactions and how – as a Leather user – you can connect to Asigna today.
What are multisig wallets and how do they work?
While a traditional crypto wallet relies on a single private key for authorization, multisignature (multisig, for short) wallets are a type of crypto wallet that require multiple private keys to authorize and complete transactions. These additional private keys give users added layers of protection against unauthorized access.
Normally, multiple participants (commonly known as “cosigners”) come together to create a multisig address. Each participant generates their own private key independently. The participants then collectively define the rules for the multisig address, including the required number of signatures (or keys) needed to validate a transaction. In this case, cosigners can be individuals, devices, or even automated scripts.
So when a participant wants to send funds from a multisig address, they would create a transaction as they would with a regular wallet. The difference here, however, is that to complete the transaction, the required number of cosigners must provide their private key signatures. If the cosigners agreed to a 2-of-3 multisig setup, then two out of three cosigners would need to use their private keys to sign off on the transaction.
What are the benefits of multisig?
The biggest benefit of multisig wallets is the added layer of security they provide.
Multisig wallets often reduce the risk associated with a single point of failure and offer more flexibility in setting security parameters. While we used a 2-of-3 multisig setup as a previous example, users can also opt for more complex setups (like a 3-of-5, 4-of-6 and so on). Additionally, in the event that one of the cosigners involved in the multisig setup loses their private key, the other cosigners can update the multisig rules to replace the lost key with a new one, which prevents a permanent loss of access to funds.
These extra layers of security are often why multisig wallets have a wide range of use cases, particularly in joint ventures and crypto custody services where multiple parties need to jointly manage funds. Additionally, they enable escrow services and secure trading between users by ensuring that all parties must agree to a transaction before it is executed.
Asigna’s native Stacks approach
As we mentioned before, Asigna is a native multisig solution for the Bitcoin main chain and the Stacks layer. This Stacks-native approach is key to the Asigna app, as it gives users the flexibility they need to connect to all sorts of applications without the potential security risks that can come with traditional multisig solutions.
For example, while smart contracts have been used in a good number of multisig solutions to add extra functionality, they also open the door to additional security risks. Asigna’s native architecture effectively reduces those risks by eliminating users’ reliance on external smart contracts or third parties.
This same Stacks-native approach also gives users the accessibility they need to connect to apps in the Stacks ecosystem. Today, Asigna users can connect to decentralized exchanges (DEXs), NFT marketplaces and more because of the app’s compatibility with the ecosystem as a whole. This also includes infrastructure developments like sBTC, which will open up additional avenues for Asigna users to interact with the app and the Stacks layer itself.
A walkthrough of Asigna Stacks multisig
To get started with Asigna’s Stacks multisig platform, you can visit the Asigna treasury and connect your Leather wallet. Simply click on the “Leather” button to begin the process.
You’ll be taken to the “Stacks Treasury” page where you can view your STX balance along with your Stacks tokens.
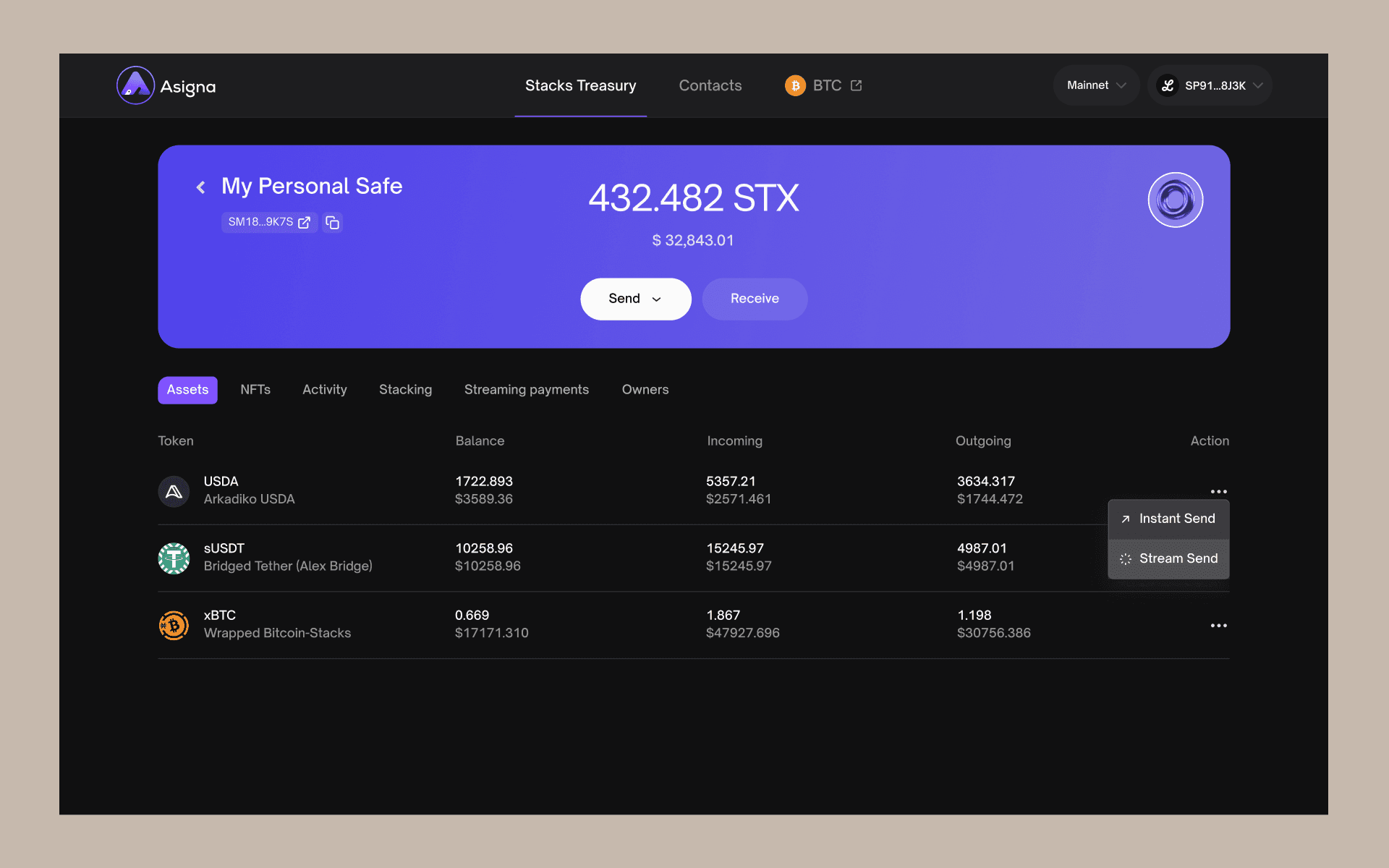
With Asigna, you can create more than one safe for your multisig STX transactions. You can give each safe a customized name and invite the necessary cosigners for each multisig setup.
Cosigners are referred to as safe “owners” once they accept your invitation.
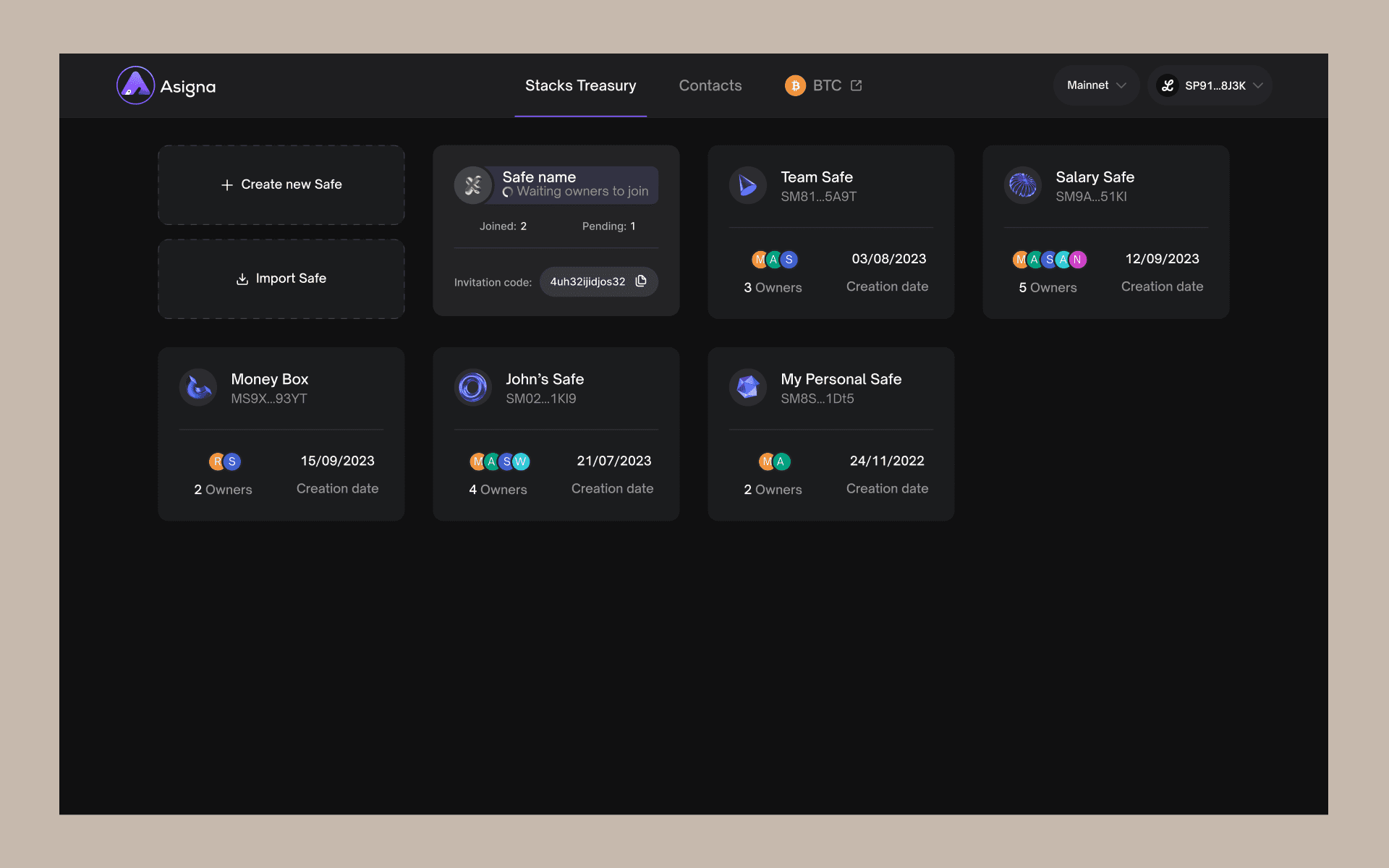
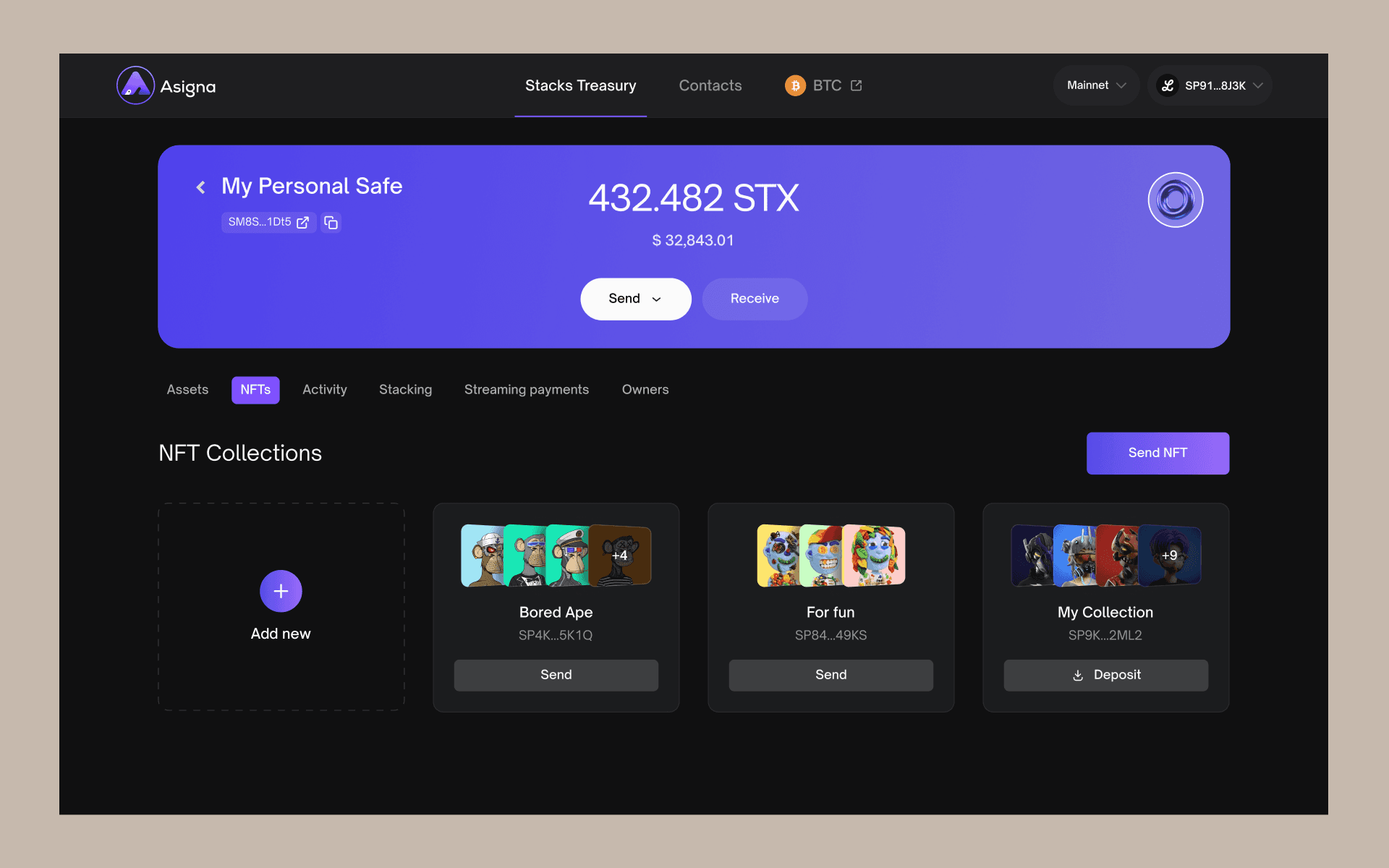
If you go back to your main Stacks Treasury page, you’ll also notice that you can also view and send your NFT collections and track your Stacking activities.
To keep track of transactions, head to the “Activity” tab. There, you’ll find a record of all past transactions along with a status tracker that helps you keep tabs on which transactions still need confirmation from all required cosigners.
Once all cosigners have confirmed a transaction, you can hit the “Execute” button to complete it.

Leather and Asigna: your multisig solution
Ultimately, our integration with Asigna’s Stacks multisig platform gives Leather users access to a native multisig solution that prioritizes security and expandability.
If you want to learn more about Asigna, you can visit their documentation page to find out more about Bitcoin multisig and Stacks multisig.
To integrate your Leather wallet with Asigna Stacks multisig today, head to the main Stacks Treasury page on the Asigna website.
Connect to web3 applications built on Bitcoin with the Leather browser extension. Install Leather – the only wallet you need to tap into the multilayered Bitcoin economy – today.
